What Is Colposcopy ?
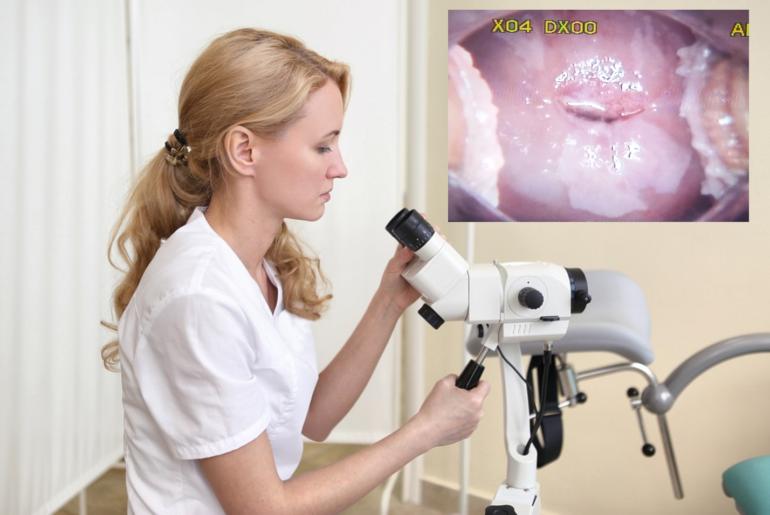
Colposcopy is a diagnostic procedure used to achieve illuminated and magnified images of cervix, vagina and vulva. A microscope named colposcope with various magnification lenses is used in this procedure.
Uyarı: +18 Doğrulama Gerekmektedir.
Görüntülemeye çalıştığınız içerik/görsel +18 doğrulama gerektirmektedir.
Eğer 18 yaş ve üzeri olduğunuzu doğruluyorsanız "e-posta" sekmesine
e-posta adresinizi yazarak, "Doğrula" butonuna tıklayınız.
“Colposcope” is in fact an enormous microscope and basic purpose is to magnify the cervix and other external genital system of the female and it is a device providing investigation of them under high light.
Investigation of cervix and vagina is based on identifying the characteristics of limits, colors and vessel structures of malignant and cancer precursor epithelium (=tissue) with colposcope. Monitoring epithelial surface with advanced methods allows the person using the colposcopy to separate the normal tissue from abnormal areas and by this means, biopsy is received from suspected regions. Colposcopy of vulva with kretinized epithelium (multi-layer epithelium tissue) allows an examination with a magnified image under clear light.
Basic purpose of colposcopy is to identify cancer precursors and lesions proceeding to cancer and to provide its treatment in early period.
To whom and when should colposcopy be performed?
In 2006, “American Society for Colposcopy ad Cervical Pathology (ASCCP)” gathered in order to create a guide based on management of women, whose cervical cancer scanning tests were abnormal and who had cervical cancer precursor lesions. Many organizations authorized and experienced in terms of women’s health and cancer were represented in this meeting. Colposcopy was recommended in adult women in accordance with below mentioned general categories:
◾ Unique abnormalities in cellular level
◾ Long-term atypical inflammation cells (ASCUS) or high risk HPV positive ASCUS
◾ Atypical cells without exclusion of high stage lesions (ASC-H)
◾ AAtypical glandular cell (AGC)
◾ Low stage squamous cell cancer precursor lesion (LSIL)
◾ High stage squamous cell cancer precursor lesion (HSIL)
◾ Invasive cancer suspicion
◾ Cancer cell existence
Additional circumstances colposcopy is necessary:
Investigation of cells (cytology) HPV test of normal patient is achieved positive for 2 consecutive years. (See “Cervix cancer scanning”, “Abnormal HPV test, normal Pap test” section)
Women, who have been exposed to diethylstilbestrol in mothers’ uteruss (However, it is now very hard to encounter these kind of patients!)
In terms of evaluating cervix, vagina or vulva observed abnormally when touched or looked by bare eyes
In order to ensure that known lesions are completely removed or treated, it may be performed in order to detect if there is any lesion around, and during conization for evaluation after treatment or in synchronization with other treatment methods.
So, what are the conditions requiring not performing colposcopy?
There is no condition to absolutely prevent application of colposcopy.
If the patient has excessive secretion, treatment is absolutely required before examination and colposcopy. Because infection causes inflammation in tissue and this condition may cause receiving biopsy from incorrect site or incorrect evaluation of the changes observed in epithelium tissue.
However, it is okay when we write it like this, it is unfortunately impossible in our day, in which we live practically and untimely. Therefore the person performing colposcopy should choose and direct the patients in accordance with his/her experience.
For instance, “Trichomonas vaginalis” may cause cervix inflammation; however, vagina infections do not prevent performing colposcopy.
Starting from this example, it should be emphasized one more time that colposcopy is a tool depending on much experience and providing information in accordance with skills, personal experience of the operator applying. Don’t quote me on it but it is the same as ultrasonography. The results achieved depend on the person performing.
Let’s pass to the main subject, how is COLPOSCOPY performed?
1.At Preparatio Stage: A very good anamnesis of the patient should be obtained. For instance; information about all medical history, fertility (how many births, abort etc.), last menstruation period, any hormones or sexual protection method including hormones used, previous cervix cytology results, HPV test results, allergies, medications used, conditions regressing the immune system (for instance, does she have ulcerative colitis or ankylosing spondylitis or blood diseases like lymphoma?) Is she treated?) and certain information including interventions made on cervix previously may be important in terms of analysis of cytology, histology and colposcopy. Allergy should be questioned. Iodine allergy is questioned the most. Therefore the women, who have iodine allergy should be determined before the procedure, so frequent usage of iodine including solutions are avoided in the examination.
Pregnancy test should absolutely be made in case thre is any suspicion about pregnancy. Curettage procedure within cervix (we call endocervical curettage briefly ECC) is NOT APPLIED in pregnant women due to a probable trauma and severe bleeding risk to birth sac.
If cervical cytlogy of the patient is performed in an out laboratory or interpreted by an unknown cytology specialist, frequently applying second cytology sampling is required to verify the cytologic diagnosis. At least classical book information is this way.
Colposcopy is performed on back position and classic gynecologic examination position, which is not liked by the women and has no aspect to be liked. After vulva is observed for whether there is any suspicious region, speculum is placed within the vagina. The most appropriate speculum should be used to observe the entire cervix and vagina.
Recent cytology evaluation carries the harmonization among cytology, colposcopy and histology to the highest degree. If cervical citology evaluation is performed less than 6 weeks, fake negative results may be achieved because renewal of sampled cervix apithelium may take 6 weeks. If necessary, HPV test may be performed on cytology sample.
3. Colposcopic Examination — Cervix and vagina are primarily observed by a bright light and then colposcope is used. Cervix covered by mucus, blood, secretion or residues is cleaned by a piece of cotton absorbed with saline (salty water) for a better vision. Cervix is controlled in order to detect probable worn regions, real leukoplakia, dark lesions, prominent ulcerated or swollen lesions before applying the solutions.
Acetic acid solution is used to heal the image of the abnormal areas. 3-5% acetic acid is applied on cervix by cotton swabs in order to ease recognition of squamocolumnar junction. Acidic liquid absorbs the fluid from inside of the cell after 30-60 seconds, wider and more intense core squamous cells (metaplastic cells, dysplasia cells, cells infected by HPV etc.) reflect the light and therefore they seem white.
Although it is understandable while we explain it in such a way, in fact we don’t why acetowhite epithelium occurs very much. On the other hand benign cellular changes depending on inflammation such as acanthosis may also cause occurrence of acetowhite epithelium.
Blood vessels and cylindrical cells are not affected but they are easily remarked on white ground. In case of need, acetic acid should be applied again after 3-5 minutes. If excessive amount of acetic acid is accumulated in vagina, it should be removed by dry cotton swabs as it may cause irritation.
Clinician performing colposcopy should primarily recognize and evaluate squamocolumnar junction, in other words transformation zone, in other words transition zone.
Squamocolumnar junction, in which gland, cylindrical tissue (columnar epithelium) of inner uterus and the tissue of vagina (squamous epithelium) come across, reveals transformation zone, in which cylindrical cells flatten. Transformation zone represents the region, in which active cell reproduction occurs, therefore it is identified by metaplasia cells. Here HPV virus likes to infect these cells.
Therefore it is the most probable place to demonstrate abnormal growth. The place of the transformation zone may vary depending on age, hormonal situations such as menopause, usage of hormones for birth control, pregnancy, previous cervix treatments and acidity degree of the vagina.
The fact that transformation zone is visible reveals that colposcopy examination is successful, in other words all squamocolumnar junction is monitored from all sides. However, if it is not monitored, then the examination is not satisfactory. Limits of all lesions, which may be monitored in addition, should be identified for a sufficient examination. This condition is identified as “insufficient colposcopy”.
Reference: This article is an article based on UpTODate.
27 Temmuz 2016 tarihinde Prof. Dr. Süleyman Engin Akhan tarafından yayınlanmış ve 20 Kasım 2018 tarihinde de son güncelleme yapılmıştır.