HPV Infections on Gays, Lesbians and Bisexuals
It is a long-known fact that HPV is the main reason for cervical cancer. Latest research show that, elevated risk HPV is also an important factor for the development of anus and oral cancer. These researches also have shown that; these cancer types are prevalent on the LGBT community due to their lifestyles and their habit of benefiting from scanning tests.
Anal Cancer
The main way of infection of HPV is through skin contact. A heterosexual relationship with vaginal penetration is not the only condition for HPV to develop. Also, most people have solved this issue through their own immune system’s reactions to the disease, without going to a clinic. But in cases such as HIV (+), where the immune system is under pressure, the body cannot cope with the virus and it causes precancerous lesions to develop. Research shows that, the frequency in which HPV is found on the anus of a heterosexual man is around 50%, while for homosexuals who are HIV (-), this ratio is around 61%. The frequency of HPV infections on homosexuals who are HIV (+) is around 93%.
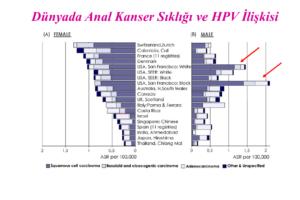
Figures below show the anal cancer frequency in San Francisco in 2006. Columns pointed out with arrows are important for emphasizing how frequent the occurances of anal cancer in San Francisco. This is due to a concentrated gay population in this area.
Yapılan bir çalışmada 6 aylık bir takip döneminde homoseksüel erkeklerde anal kansere neden olduğu bilinen HPV lerden biri olan HPV tip16 ile enfekte olma riskinin diğer popülasyona göre 6.5 kat daha fazla olduğu saptanmıştır. Anal HPV enfeksiyonunun persiste etmesinin de erkek eşcinsellerde daha sık oluğu bilinmektedir (%32 vs. %4). Bu verilerden de anlaşılabileceği gibi anal kanser nedenlerinden olan HPV nin daha sık görüldüğü homoseksüellerde, anal kanser sıklığı heteroseksüel erkeklere göre daha fazladır.
The figures below summarize these findings.
Cervical cancer is 8 in 100.000 for women; anal cancer is 0.8 in 100.000 for heterosexual men, 35 in 100.000 for homosexual HIV (-) men and 70 in 100.000 for homosexual HIV (+) men.
Risk factors for anal cancer is not different than for cervical cancer. Basic risk factors: cigarettes, passive homosexual relations, having genital warts, Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 infection, Hepatitis B and C or being chronically ill, chlamydia infection and most importantly being HIV (+) meaning having AIDS.
HPV types 18 and/or 16 are detected in 72% of all anal cancers.
HPV causes anal cancer with the same cycle that it causes cervical cancer. The high risk YPV types start the cancer process by causing precancerous lesions to form.
Just like in cervical cancer, these precancerous lesions can be detected by “anal smear” and the treatment process can be started. This is the reason why men and women who have anal sex are recommended a smear test every 2-3 years by some centers.
HIV (+) patients that actively have anal sex, must have the smear done each year.
But, anal smear process is not as universally accepted around the world like mouth smear test. As there is no universally accepted test method for gay and bisexual men, these individuals need to consult their health professional and might be required to have additional methods applied.
How anal smear is taken?
The patient gets into a position to have their anal examination (if the patient is a woman, firstly cervical smear is taken)
The immediate anus area and the surrounding areas will be evaluated for active lesions (the buttocks need to be opened towards the sides by hand for this examination) Dacron refuse collector or a brush should be placed, entering the anus for around 2.5 to 5 cms. The anal smear will be taken by twisting it 360 degrees.
The collected material will be wiped on the microscope glass and fixed with alcohol.
It should be sent for pathologic examination, mentioning that the material is taken from the anus. If the result comes back as HPV positive or anal dysplasia, an anal colposcopy, where the anus is examined with a solution and lens should be done, in addition to a biopsy.
Protection
The protection from HPV related cancers include; Firstly, getting information on sexually transmitted diseases, changing behaviors and getting vaccinations, secondly the diagnosis and treatment of precancerous lesions.
Use of condoms also decrease the chance of HPV infections. But the condoms only protect the body of the penis. The protection of vulva areas is done by body hair. And we shave these hair under the name of ‘hygiene’. By doing so, you provide the perfect conditions for infection if your partner has warts.
This is why it is a common sight to see this sentence on the books or the internet: “Since HPV is infected through skin contact and the condom doesn’t cover the whole skin area, use of condoms is not a definitive preventive solution in order to avoid HPV.” This is not true. Then you should stay “hairy”! Please do not shave. They are there for a reason!
On the other hand, although monogamy and decreasing the number of sexual partners, help reduce the risk of HPV infections, you should know that it’s not a definitive solution. You know the old saying; “No one is infallible”
Therefore, you should always take the necessary precautions. These suggestions are not only for homosexuals, but general suggestions that reduce the risk of HPV infection overall.
The best way of protection is HPV vaccination. Only quadruple effect HPV infections are available on the market now. This vaccination provides protection against four types of HPV (Types 16-18-6 and 11) This is a preventive precaution, not one that is used towards treating the disease. Therefore, the target segment for vaccinations are teenagers, the naïve and virgin population. But sexually active individuals can get vaccinations too. It is important to note that the preventive features are weaker for these people.
Tens of research conducted until this point show that gays and lesbians cannot access the HPV vaccinations (at least in the USA). Let’s not talk about the situation in our country. If you can access it, quadruple effect HPV vaccinations are also effective on gay individuals.
Lesbians and Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is more frequent in lesbian women, compared to heterosexual women. The widely accepted view on this is can be summed up as; “The fact that lesbians are more likely to skip on routine gynecologist examinations, in addition to lackingbasic information about their anatomy”, but I am among those who think it’s not as simple as that.
First of all, it is known that many lesbians also have had heterosexual relations at some point. Therefore, it is safe to assume that HPV is primarily infected by a male. On the other hand, the HPV infection for females happens on skin contact.
Skin contact includes; genitals touching each oter, touching her or her partner’s genital, oral sex or vibrators or similar use of sex toys without proper cleaning beforehand or using them with different partners. Despite this risk factos, according to US data lesbians are less likely to have their gynecologic examinations and know less about infections that are caused by sex. Lesbian women also need to have their cervical vaccination and pap-smear, which is a cervical cancer monitoring test.
The prevention of HPV and HPV related cancers for LGBT community is also by PAP smear tests and vaccinations. This situation is also the same for males who are under the risk of HPV infection.
FDA have approved the use of HPV vaccination for men too. Experienced doctors on anal cancer and homosexuals, also suggest the anal smear test, which is taking cell camples from the anus and starting the treatment for the lesions which are likely to turn into cancerous cells.
The reason these suggestions are not globally accepted and approved, is because the necessary work have not been carried out.
The facts that lesbians do not do smear tests routinely, the gays are not aware of anal smars or vaccinations, are the main reasons why HPV is more likely to infect LGBT community.
3 Şubat 2013 tarihinde Prof. Dr. Süleyman Engin Akhan tarafından yayınlanmış ve 27 Haziran 2018 tarihinde de son güncelleme yapılmıştır.